Interview with Chunyi Zhi
Get em-powered up
Chunyi Zhi, associate professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, City University of Hong Kong, who is currently focused on flexible/wearable energy storage devices and sensors, and has published more than 190 papers, talks with Savita Verma about the yarn batteries and their future.
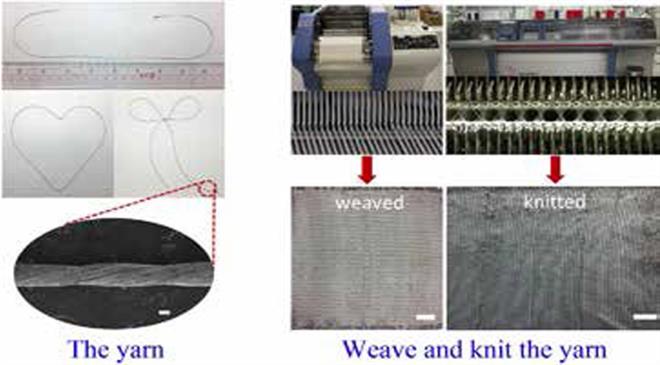
There has been search for rechargeable textile based batteries to simplify the next generation personalised wearable electronics. Development of such batteries has been hampered by the lack of industrially weavable and knittable highly conductive yarns. This is what has been achieved by Dr Chunyi Zhi and Dr Yan Huang from the City University of Hong Kong and their team. They have produced highly conductive yarns and used them to fabricate a yarn battery with state-of-the-art performance in terms of capacity, energy density, power density, and rate capability. The scientists have weaved these yarns to make a wristband battery which could power various electronic devices such as watches and LEDs, enabling dual functions of wearability and energy storage. Zhi believes that the yarn battery will be useful in wearable electronics, smart garments, and in healthcare in the future. The next in line is improving these batteries to make them washable, water-proof, and durable, taking them closer to commercialisation. The highly conductive yarns are uniformly covered with zinc (as anode) and nickel cobalt hydroxide nanosheets (as cathode). The yarn is strong enough to be woven and knitted by both machine and hand.
TT: High-performance wearable nickel/cobalt-zincbased batteries are already known as an excellent source of power for personalised wearable electronics. You have developed yarn to facilitate development of such a battery. Could you elaborate what this yarn is?
This yarn is drawn and twisted by ultrathin stainless steel 316L filaments which are spun at high temperature. Since the source of yarn is stainless steel, it is inherently highly conductive.
TT: What next are you planning? Are you planning to commercialise or carry out some more studies?
Yes. We plan to commercialise. Before commercialisation, we need to carry out more textile-related studies, such as air permeability, washability, etc, and solve technical issues regarding wearing comfortability and safety, etc.
TT: Could you explain a little about use of this yarn battery in sensors and other medical uses? What kind of sensors? How will this battery make life easy for users of these sensors?
As most sensors are electronic devices, they need a battery to work. So, we use our yarn battery to power these electronics such as pulse sensor, watch, LED, etc. The pulse sensor can detect the pulse frequency of our heart. Most current batteries are rigid, so they are not flexible and cannot be wearable.
TT: Does it mean that all of the conductive yarn is a battery or you need to do something to make a battery out of the conductive yarn?
The conductive yarn is an electrode. With two such electrodes and electrolyte, a battery is made.
TT: How do you see its use in practical situations? How does the battery benefit the users in comparison to the current scenario?
This high-performance wearable battery imposes two considerable requirements for yarn electrodes: high electric conductivity and high mechanical strength. Although many conductive yarns have been demonstrated (for example, repetitive surface coating of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and metals, spinning of carbonaceous materials, etc), the two desirable features for batteries are not possessed at least simultaneously, besides the cost-expensive and time-consuming limitations.
TT: What is the benefit of making a full dress of this battery or making battery part of a dress? What purpose will it serve?
When a dress is a battery, the dress itself can power various portable, flexible and wearable electronics, such as our smart phone, our medical sensor, etc.
TT: Do you see this development useful for fashion industry?
Yes. We believe it will be used in fashion industry.
TT: Your paper mentions a wrist band battery. How is it made? Does it mean that wrist band itself is made up of this yarn? Is the band itself a battery, or the battery is part of the band?
The wrist band itself is made up of a cloth weaved by this yarn. The band is an assembly of five cloth batteries in series.
TT: What is the significance of the battery being rechargeable? How does it help users?
The rechargeability is very important for batteries because it means sustainable use and low cost.
TT: What kind of use is possible for this battery or yarn in fashion industry? Please explain a bit.
The battery can serve as a power source in a fashion garment. The yarn can serve as an electronic conductor in fashion garment.
TT: Could you tell why do we need a power source in a fashion garment or an electronic conductor? What kind of fashion garments? What is the effect for which this battery needs to be embedded in a fashion garment. How will it enhance its fashion quotient?
The yarn battery can work as a power source; then you don't need an extra one. Between the yarn battery and electronic devices embedded in the garment, you may need conductive yarn to connect them. That is, it needs a conductive yarn to connect the yarn battery with the electronic devices so that the yarn battery can power them. For fashion, you may need electronic devices, such as LEDs, lighting devices, displays (e-ink type or LCD) to enhance their fashion. Moreover, some health monitoring garments may incorporate some sensors, such as strain sensor, UV light sensor, pressure sensor, etc. Our battery can also be used to power these sensors.
TT: As you say this battery needs to be charged. Therefore, if a wrist watch is made using this yarn as battery, it will need to be charged first. And then once the battery is used completely, it can be charged again. There is no need to replace the battery? Is that the benefit you talk about?
Yes, exactly. Therefore, we call it "rechargeable".
TT: And how is it recharged?
With a power source such as a DC power supply providing current/voltage, the battery is recharged.
TT: What all uses you see for this battery? Is it meant for medical purposes and how?
The textile battery can be worn to charge various electronic devices, such as watch, sensor, etc. It is not just for medical purposes.
TT: Do you see clothes or dresses with this kind of a battery? If you make a dress of this yarn, will the dress itself behave as a battery? Or battery will be embedded in part of the dress?
We haven't seen clothes or dresses with this kind of a battery. If all technical issues regarding wearing comfortability and safety etc are solved, the dress itself can be a battery. The battery can also be embedded in part of the dress.